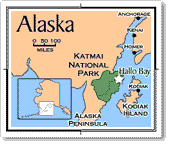
Enjoy the video coverage of KTVA on Hallo Bay Bear Camp habitat preservation.
Wednesday, July 23, 2014
Monday, July 21, 2014
Sunday, July 20, 2014
Wolves
A light-reflecting layer on a wolf’s eye called the tapetum
lucidum (Latin for “bright tapestry”) causes a wolf’s
eyes to glow in the dark and may also facilitate night vision.
While a wolf’s color perception and visual acuity maybe be
inferior to a human’s, a wolf’s eyes are extremely sensitive to
movement.
Saturday, July 19, 2014
Friday, July 18, 2014
Chum Salmon
Chum salmon, also known as dog salmon, are the most widely
distributed of all the Pacific salmon and generally occur
throughout Alaska. Like most other Pacific salmon species,
chum salmon spend most of their life feeding in saltwater,
then return to freshwater when mature to spawn once in the
fall then die. Most chum salmon populations do not travel far
upstream to spawn; however, some travel up to 2,000 miles
upstream to the headwaters of the Yukon River. Although
generally regarded as one of the less desirable species of
salmon, in Arctic, Northwestern, and Interior Alaska, chum
salmon are highly prized as a traditional source of dried
winter food. Since the 1980s, commercial chum salmon harvests
in Alaska have more than doubled as a result of the Alaska
hatchery program and increased foreign sales.
Thursday, July 17, 2014
Ravens in Alaska
Ravens are excellent fliers, engaging in aerial
acrobatics and sometimes soaring to great heights. Flight
is often an alternation of wing flapping and gliding and
is deceptively fast, as ravens move quickly with seemingly
slow wing beats. In courtship flights ravens fly with
wingtips touching, and repeatedly dive and tumble
together.
There is no mistaking the raucous call of the raven; the deep, resonant “kaw” or “prruk prruk prruk” is its trademark. However, the raven can produce an amazing assortment of sounds: mews, whistles, high-pitched cries, “glooks,” and dripping water sounds. One study in Alaska showed ravens have more than 30 distinct vocalizations.
There is no mistaking the raucous call of the raven; the deep, resonant “kaw” or “prruk prruk prruk” is its trademark. However, the raven can produce an amazing assortment of sounds: mews, whistles, high-pitched cries, “glooks,” and dripping water sounds. One study in Alaska showed ravens have more than 30 distinct vocalizations.
Wednesday, July 16, 2014
Tuesday, July 15, 2014
Monday, July 14, 2014
Saturday, July 12, 2014
Wolf facts
- In the Harry Potter universe, werewolf Remus Lupin’s name is directly related to the Latin word for wolf (lupus) and suggests an association with one of the founders of Rome, Remus, who was suckled by a wolf. The dual nature of Lupin’s werewolf nature suggests that in the Potter realm, there are two sides to everything.
- The last wolf in Yellowstone Park was killed in 1926. In 1995, wolves were reintroduced and, after just ten years, approximately 136 wolves now roam the Park in about 13 wolf packs.
- Currently, there are about 50,000 wolves in Canada; 6,500 in Alaska; and 3,500 in the Lower 48 States. In Europe, Italy has fewer than 300; Spain around 2,000; and Norway and Sweden combined have fewer than 80. There are about 700 wolves in Poland and 70,000 in Russia.
Friday, July 11, 2014
Ermine in Alaska
Ermine are adapted to a wide variety of habitats. It
prefers wooded areas with thick understory near
watercourses, and often occupies early-successional or
forest-edge habitats, wet meadows, marshes, ditches,
riparian woodlands, or river banks with high densities
of small mammals and adequate subnivean foraging
space. Coastal ermine may exhibit a preference for low
elevation riparian and marine shoreline and estuarine
habitats. They are well-adapted to snowy environments
and range into alpine areas. They have been documented
year-round living at 2,000–3,000 ft in the Sierra
Nevada, California and also successfully inhabit
tundra habitats throughout northern Canada and Alaska.
Thursday, July 10, 2014
Wednesday, July 9, 2014
Monday, July 7, 2014
Bird Facts
- Birds play a central role in many creation myths. Birds are also often associated with the journey of the soul after death or as mediators between the dead and living. They can also appear as oracles or tricksters.
- The game Angry Birds has sold more than 7 million copies on Apple’s iPhone. The game was made by a team of just four people. It was such a low priority for the company that it took over 8 months to finish.
- Wind farms kill approximately a half-million birds per year in the United States, according to a 2008 Fish and Wildlife study. Nearly 10,000 birds, almost all of which are protected by the migratory bird acts, are killed every year at the wind farm in Altamont Pass, CA, alone.
- Approximately 200 people have died since 1988 because of airborne collision between airplanes and birds. Bird strikes cause $300 million of damage each year to aircraft. The first recorded bird strike was in 1905, when Orville Wright’s plane hit a bird and killed it.
Sunday, July 6, 2014
Leave No Trace Camping and Hiking
1. Trash your Trash
Put litter—even crumbs, peels and cores— in garbage bags and carry it home or throw it in trash receptacles. Extra food, even apple cores and banana peels can do great damage to wildlife. Did you know it takes up to two years for orange or banana peels to decompose in nature; more than 10 years for plastic bags and more than 80 years for aluminum cans to decompose?
2. Dog Dogma
Use a plastic bag to pack out your dog’s poop to a garbage can. Dog waste can be harmful to the natural environment and can cause the spread of invasive species.
3. Take Only Pictures. Leave Only Footprints
According to U.S. state and national park services, Americans logged 1.6 billion visits to national and state park lands last year. If we all took a memento from nature during those visits, the landscape would change. Fill the memory card on your camera rather than your pockets and leave nature as you found it for others to enjoy.
4. Keep Wildlife Wild
Human food is unhealthy for all wildlife and feeding them can have unfortunate consequences such as drawing them to people and roads and making them sick.
5. Refuse the Makeover
No need for a major remodel of nature. Bring your own lightweight camp or picnic furniture and conveniences such as camp gas stoves, sleeping pads, chairs and lanterns. When you leave, it should look as though you were never there.
Put litter—even crumbs, peels and cores— in garbage bags and carry it home or throw it in trash receptacles. Extra food, even apple cores and banana peels can do great damage to wildlife. Did you know it takes up to two years for orange or banana peels to decompose in nature; more than 10 years for plastic bags and more than 80 years for aluminum cans to decompose?
2. Dog Dogma
Use a plastic bag to pack out your dog’s poop to a garbage can. Dog waste can be harmful to the natural environment and can cause the spread of invasive species.
3. Take Only Pictures. Leave Only Footprints
According to U.S. state and national park services, Americans logged 1.6 billion visits to national and state park lands last year. If we all took a memento from nature during those visits, the landscape would change. Fill the memory card on your camera rather than your pockets and leave nature as you found it for others to enjoy.
4. Keep Wildlife Wild
Human food is unhealthy for all wildlife and feeding them can have unfortunate consequences such as drawing them to people and roads and making them sick.
5. Refuse the Makeover
No need for a major remodel of nature. Bring your own lightweight camp or picnic furniture and conveniences such as camp gas stoves, sleeping pads, chairs and lanterns. When you leave, it should look as though you were never there.
Friday, July 4, 2014
Thursday, July 3, 2014
Alaska Brown Bears
Brown and grizzly bears are classified as the same species
even though there are notable differences between them. Kodiak
bears (brown bears from the Kodiak Archipelago) are classified
as a distinct subspecies (U. a. middendorffi) from
those on the mainland (U. a. horribilis) because they
have been isolated from other bears since the last ice age
about 12,000 years ago. “Brown bears” typically live along the
southern coast of the state where they have access to
seasonally abundant spawning salmon. The coastal areas also
provide a rich array of vegetation they can use as food as
well as a milder climate. This allows them to grow larger and
live in higher densities than their “grizzly” cousins in the
northern and interior parts of the state.
Wednesday, July 2, 2014
Tuesday, July 1, 2014
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.JPG)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
.JPG)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
.jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
+(Small).jpg)
+(Small).jpg)




 Alaska Time
Alaska Time